What Are Accruals? How Accrual Accounting Works, With Examples
Often, however, the timing of a payment may differ from when it’s received or an expense is made, so accrual and deferral methods are used to adhere to accounting principles. As the company fulfills its obligation—whether that’s shipping a product, providing a service, or anything else it was paid to do—it gradually reduces the liability on its balance sheet. Correspondingly, it recognizes that amount as revenue on its income statement. By the time the company has completely fulfilled its obligation, the deferred revenue balance will have been fully shifted to earned revenue. Under the accrual basis of accounting the account Supplies Expense reports the amount of supplies that were used during the time interval indicated in the heading of the income statement.
- For example, you could ask your bank to charge your company’s checking account at the end of each month with the current month’s interest on your company’s loan from the bank.
- This revenue is recognized when the delivery of goods or services actually takes place.
- Though a company will have to monitor the monthly activity, this frees up analysts time to scrub their financial reports.
- The IRS requires that you follow specific rules; otherwise, the asset owner is not allowed to defer gains, which results in large tax bills.
- Deferred revenue is recorded as a liability on the balance sheet, and the balance sheet’s cash (asset) account is increased by the amount received.
See advice specific to your business
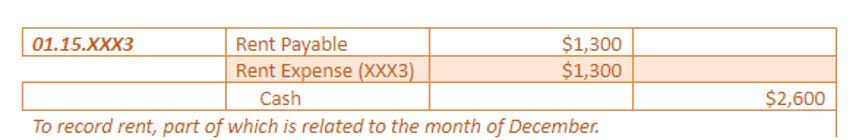
In cash accounting, you would recognize the revenue when it comes in (during Q4) but not the expense for the products you purchased until you paid for them, which might not be until Q1 of the following year. Using the accrual method, you would account for the expense needed in pursuit of revenue. Let’s say a customer makes an advance payment in January of $10,000 for products you’re manufacturing to be delivered in April. You would record it as a debit to cash are deferrals shiwn kn balance sheet? of $10,000 and a deferred revenue credit of $10,000. The recognition of a deferral results when a customer paid for a product or service in advance, or when a company made a payment to a supplier or vendor for a benefit expected to be received in the future. In all subsequent months, cash from operations would be $0 as each $100 increment in net income would be offset by a corresponding $100 decrease in current liabilities (the deferred revenue account).
How to Present an Income Statement on the Gains on the Sales of Assets
- In this article we explain the differences between accrued and deferred income and how we adjust the journal entries for them.
- Correspondingly, it recognizes that amount as revenue on its income statement.
- Monthly, the accountant records a debit entry to the deferred revenue account, and a credit entry to the sales revenue account for $100.
- Deferred expenses, much like deferred revenues, involve the transfer of cash for something to be realized in the future.
- Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI’s full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
- The other company involved in a prepayment situation would record their advance cash outlay as a prepaid expense, an asset account, on their balance sheet.
Deferred expenses, much like deferred revenues, involve the transfer of cash for something to be realized in the future. Deferred revenues refer to money received for goods or services to be provided to customers later, whereas deferred expenses refer to money expended for obligations not yet observed. When payment is received in advance for a service or product, the accountant records the amount as a debit entry to the cash and cash equivalent account and as a credit entry to the deferred revenue account. When the service or product is delivered, a debit entry for the amount paid is entered into the deferred revenue account, and a credit revenue is entered to sales revenue. For example, a company with a bond will accrue interest expense on its monthly financial statements, although interest on bonds is typically paid semi-annually. The interest expense recorded in an adjusting journal entry will be the amount that has accrued as of the financial statement date.
Deferred Revenue
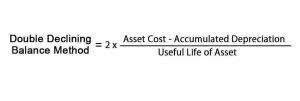
If you buy inventory, you debit cash to pay for the new credited asset, the inventory. The new asset is a credit that is offset in an equal amount, with the deferred gain debit. A company acquires a machine that costs $60,000, and which has a useful life of five years. This means that it must depreciate the machine at the rate of $1,000 per month. For https://www.bookstime.com/ the December income statement at the end of the second year, the monthly depreciation is $1,000, which appears in the depreciation expense line item. For the December balance sheet, $24,000 of accumulated depreciation is listed, since this is the cumulative amount of depreciation that has been charged against the machine over the past 24 months.
The Accrual Method of Accounting
Deferred revenue is a liability because it reflects revenue that has not been earned and represents products or services that are owed to a customer. As the product or service is delivered over time, it is recognized proportionally as revenue on the income statement. The accrual of expenses and liabilities refers to expenses and/or liabilities that a company has incurred, but the company has not yet paid or recorded the transaction. The accrual of an expense will usually involve an accrual adjusting entry that increases a company’s expenses and increases its current liabilities.
- In either case, the company would repay the customer, unless other payment terms were explicitly stated in a signed contract.
- No, in cash basis accounting revenue is reported only after it has been received.
- Accountants also use the term “accrual” or state that they must “accrue” when discussing revenues that fit the first scenario.
- The payment is considered a liability because there is still the possibility that the good or service may not be delivered or the buyer might cancel the order.
- Accounting principles require the revenues and expenses are recorded when they are incurred.
An accrual system recognizes revenue in the income statement before it’s received. A deferral system aims to decrease the debit account and credit the revenue account. Accruals are when payment happens after a good or service is delivered, whereas deferrals are when payment happens before a good or service is delivered. An accrual will pull a current transaction into the current accounting period, but a deferral will push a transaction into the following period. Having received the payment, the company is set to deliver the equipment between January 1 and February 27.
Let us look at a detailed example of the accounting entries a company makes when deferred revenue is created and then reversed or earned. So, it can be concluded that because of the prepayment of insurance the company reports $15,000 as deferred expenses until June 15; when the next payment will be scheduled. So while both involve a delay, deferred payment deals with the timing of the payment, and deferred revenue pertains to the timing of revenue recognition. Deferral is also used to describe the type of adjusting entries used to defer amounts at the end of an accounting period. For example, a contractor might use either the percentage-of-completion method or the completed contract method to recognize revenue. Under the percentage-of-completion method, the company would recognize revenue as certain milestones are met.
Recording Common Types of Adjusting Entries
- This would involve debiting the “accounts receivable” account and crediting the “revenue” account on the income statement.
- However, your balance sheet will show an accumulated depreciation value of $60,000, since that is what has added up in the 30 months you’ve had this asset.
- Once the payment has been made in the new year, the liability account will be decreased through a debit, and the cash account will be reduced through a credit.
- Operating liabilities are amounts owed resulting from a company’s normal operations, whereas non-operating liabilities are amounts owed for things not related to a company’s operations.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!